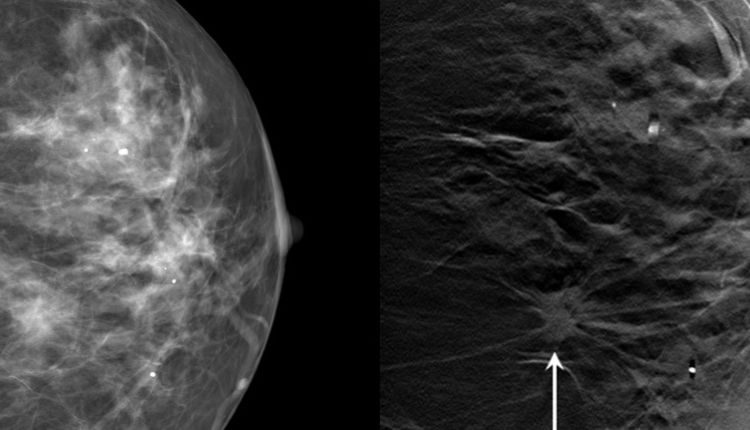
Breast cancer is a global health concern that affects millions of women worldwide. It is the most common cancer among women, and early detection is crucial in managing the disease effectively. One of the most innovative and promising tools in this fight against breast cancer is 3D mammography, also known as digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT). This technology has revolutionized the way we approach breast cancer screening and diagnosis, offering a more comprehensive view of the breast tissue and aiding in early detection.
Traditional 2D mammography has been the standard for breast cancer screening for many years. However, it has its limitations. The primary issue with 2D mammography is that it provides only two images of the breast, from top to bottom and side to side. This can sometimes result in overlapping tissue, which can obscure or mimic tumors, leading to false positives or missed cancers.
Enter 3D mammography. This advanced technology takes multiple images or ‘slices’ of the breast from different angles, creating a layered three-dimensional view of the breast tissue. This allows radiologists to examine the breast tissue one thin layer at a time, almost like flipping through pages of a book. This detailed view helps to distinguish harmless abnormalities from real tumors, reducing false positives and unnecessary biopsies.
The role of 3D mammography in early detection of breast cancer cannot be overstated. Studies have shown that 3D mammography detects up to 40% more invasive cancers compared to 2D mammography alone. It is particularly beneficial for women with dense breast tissue, where cancer can be harder to detect using traditional methods.
Moreover, 3D mammography has been shown to improve the detection rate of smaller tumors which are less likely to have spread to lymph nodes, thus improving prognosis and survival rates. By detecting breast cancer in its earliest stages, when it is most treatable, 3D mammography plays a crucial role in reducing the mortality rate associated with this disease.
Despite the clear benefits of 3D mammography, it is not without its challenges. The primary concern is radiation exposure. While the radiation dose for a 3D mammogram is slightly higher than that of a 2D mammogram, it is still well within the safe limits defined by the FDA. Furthermore, as technology advances, efforts are being made to reduce the radiation dose while maintaining image quality.
Another challenge is access and cost. Not all healthcare facilities have access to this advanced technology, and not all insurance companies cover 3D mammograms. However, as awareness about the benefits of 3D mammography grows, more insurance companies are beginning to cover it and more facilities are investing in this technology.
In conclusion, 3D mammography represents a significant advancement in breast cancer screening and diagnosis. Its ability to provide a more detailed view of the breast tissue aids in early detection and reduces false positives, leading to better patient outcomes. While challenges exist in terms of radiation exposure and access, the benefits of 3D mammography far outweigh these concerns.
As we continue to wage war against breast cancer, tools like 3D mammography will be at the forefront of our arsenal. By promoting early detection and accurate diagnosis, we can improve survival rates and quality of life for millions of women worldwide. The role of 3D mammography in this fight cannot be understated – it is not just a tool for detection but a beacon of hope for those living in the shadow of breast cancer.